Functional groups have different priorities when it comes to naming. They are assigned priorities based broadly on their reactivity. So for example a carboxylic acid will have a higher priority than an alkene or alkyne. The highest priority functional group will be the molecule’s overall suffix and will determine the class of the molecule.
Drawing Organic Structures Functional Groups Constitutional Isomers – ppt video online download
Some functional groups have only carbon-carbon double or triple bonds; others have halogen atoms; and still others contain oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. Much of the chemistry you’ll be studying is the chemistry of these functional groups. Functional Groups with Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds

Source Image: pressbooks.bccampus.ca
Download Image
Oct 31, 2023Ketones and aldehydes are two closely related carbonyl-based functional groups that react in very similar ways. In a ketone, the carbon atom of a carbonyl is bonded to two other carbons. In an aldehyde, the carbonyl carbon is bonded on one side to a hydrogen, and on the other side to a carbon. The exception to this definition is formaldehyde

Source Image: studocu.com
Download Image
Solved 4. Six different molecules are drawn below in | Chegg.com Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices. 2.3 Functional Groups F unctional groups are the most reactive parts in organic compounds and determine the major properties of compounds. A summary of common functional groups is included in Table 2.2.

Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
Which Of The Following Molecules Contain The Same Functional Groups
Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices. 2.3 Functional Groups F unctional groups are the most reactive parts in organic compounds and determine the major properties of compounds. A summary of common functional groups is included in Table 2.2. A distinctive set of physical and chemical properties is imparted to molecules that contain a functional group composed of three pairs of doubly bonded atoms (usually all carbon atoms) bonded together in the shape of a regular planar (flat) hexagon.The hexagonal ring is usually drawn with an alternating sequence of single and double bonds. The molecule benzene, C 6 H 6, first discovered by
66 Aromatic Ketone Images, Stock Photos, 3D objects, & Vectors | Shutterstock
The letter R represents the rest of the ” R est of the molecule“, typically a hydrocarbon chain or ring. Table 11.7. 1: Selected Organic Functional Groups. NOTE: There are others, but the organic functional groups introduced in this chapter are those most often discussed in later biochemistry chapters. A Level Chemistry: Carbonyl Compounds | Teaching Resources

Source Image: tes.com
Download Image
Solved 6.) Circle any and all functional groups present in | Chegg.com The letter R represents the rest of the ” R est of the molecule“, typically a hydrocarbon chain or ring. Table 11.7. 1: Selected Organic Functional Groups. NOTE: There are others, but the organic functional groups introduced in this chapter are those most often discussed in later biochemistry chapters.
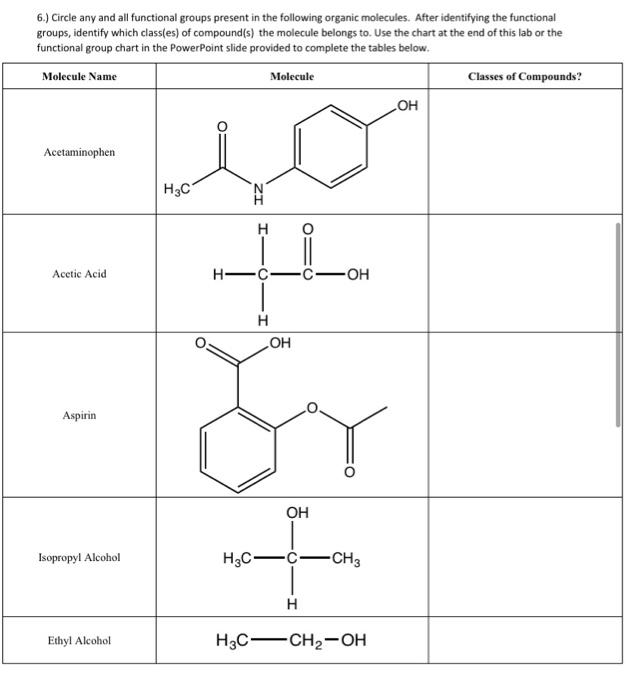
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Drawing Organic Structures Functional Groups Constitutional Isomers – ppt video online download Functional groups have different priorities when it comes to naming. They are assigned priorities based broadly on their reactivity. So for example a carboxylic acid will have a higher priority than an alkene or alkyne. The highest priority functional group will be the molecule’s overall suffix and will determine the class of the molecule.
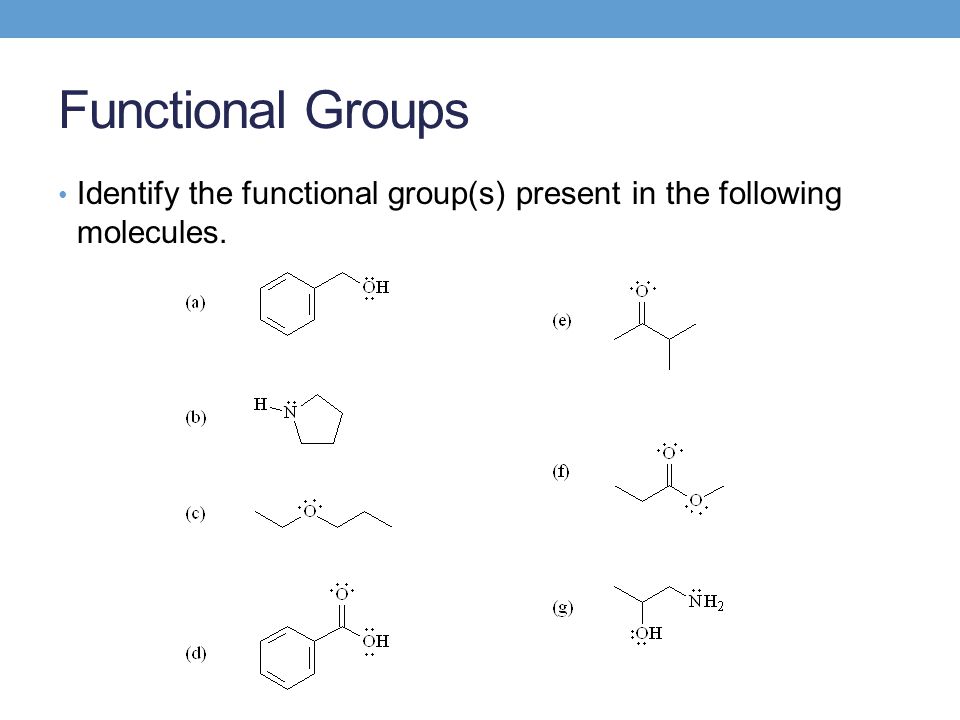
Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Solved 4. Six different molecules are drawn below in | Chegg.com Oct 31, 2023Ketones and aldehydes are two closely related carbonyl-based functional groups that react in very similar ways. In a ketone, the carbon atom of a carbonyl is bonded to two other carbons. In an aldehyde, the carbonyl carbon is bonded on one side to a hydrogen, and on the other side to a carbon. The exception to this definition is formaldehyde
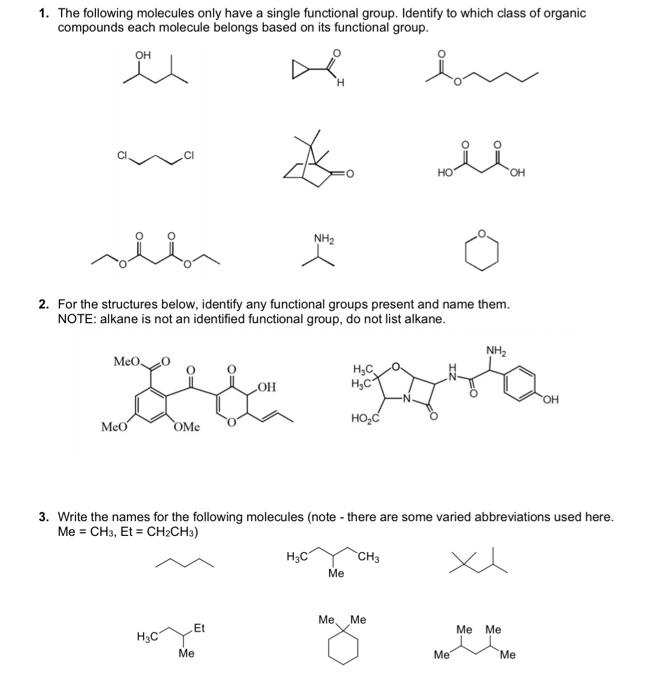
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
10.2 Functional Groups – CHEM 1114 – Introduction to Chemistry In the alcohol functional group, a carbon is single-bonded to an OH group (the OH group, by itself, is referred to as a hydroxyl). Except for methanol, all alcohols can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary. In a primary alcohol, the carbon bonded to the OH group is also bonded to only one other carbon.

Source Image: pressbooks.bccampus.ca
Download Image
5. Which of the following molecules contain the same functional groups? CH3CH(NH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2NH2 CH3CH2CONH2 CH3CH NHCH3 I III IV O O O O I, II, IV I, II, III II, III, IV I, III, IV Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices. 2.3 Functional Groups F unctional groups are the most reactive parts in organic compounds and determine the major properties of compounds. A summary of common functional groups is included in Table 2.2.

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
10.2 Functional Groups – CHEM 1114 – Introduction to Chemistry A distinctive set of physical and chemical properties is imparted to molecules that contain a functional group composed of three pairs of doubly bonded atoms (usually all carbon atoms) bonded together in the shape of a regular planar (flat) hexagon.The hexagonal ring is usually drawn with an alternating sequence of single and double bonds. The molecule benzene, C 6 H 6, first discovered by

Source Image: pressbooks.bccampus.ca
Download Image
Solved 6.) Circle any and all functional groups present in | Chegg.com
10.2 Functional Groups – CHEM 1114 – Introduction to Chemistry Some functional groups have only carbon-carbon double or triple bonds; others have halogen atoms; and still others contain oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. Much of the chemistry you’ll be studying is the chemistry of these functional groups. Functional Groups with Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds
Solved 4. Six different molecules are drawn below in | Chegg.com 5. Which of the following molecules contain the same functional groups? CH3CH(NH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2NH2 CH3CH2CONH2 CH3CH NHCH3 I III IV O O O O I, II, IV I, II, III II, III, IV I, III, IV In the alcohol functional group, a carbon is single-bonded to an OH group (the OH group, by itself, is referred to as a hydroxyl). Except for methanol, all alcohols can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary. In a primary alcohol, the carbon bonded to the OH group is also bonded to only one other carbon.